Unraveling the World of AI Agents: A Beginner's Guide
Overview
Have you ever wondered how automated amazon helpdesk understands and prompts you with contextual options? That seamless coordination is the result of AI processing behind the scenes, diligently checking other calendars and proactively suggesting available timings.
But AI agents are more than just for help desk services. They’ve quietly evolved over the past year, riding the wave of technological advancements in large language models (LLMs). As GPT-3 and GPT-4 flex their linguistic capabilities, AI agents are stepping into the spotlight, creating a buzz in the market.
The No-Code Revolution
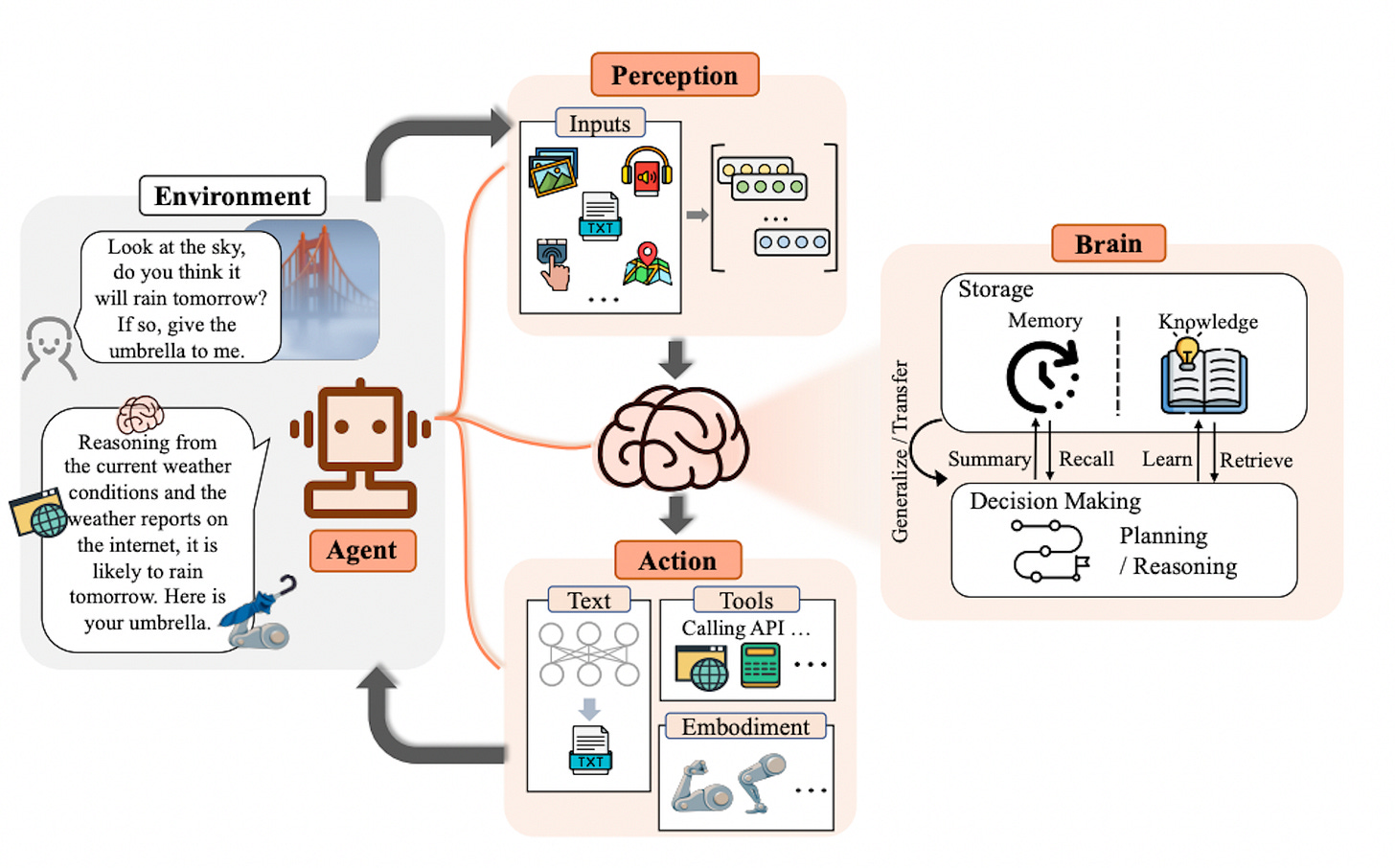
At their core, AI agents are problem solvers. They excel at breaking down complex goals into smaller tasks, reason about the best course of action, and execute a series of steps to achieve the desired outcome – all while aligning with the overarching goal defined by their human creators. Here’s how they operate:
Decomposition: When faced with a daunting task, an AI agent dissects it into smaller, digestible pieces. Whether it’s scheduling a meeting or optimizing supply chains, the agent identifies the building blocks.
Reasoning: Armed with knowledge from vast language models, the agent reasons about the best course of action. It considers context, constraints, and user preferences. Should we prioritize the morning slot for the client call? Is the warehouse closer to the supplier’s location?
Execution: Like a diligent assistant, the AI agent executes a series of steps. It sends invites, adjusts time zones, and nudges participants—all while ensuring alignment with the overarching goal. Efficiency is its mantra.
You, as a human creator defines the goal. Maybe it’s streamlining customer support inquiries or optimizing ad campaigns. The AI agent listens, learns, and aligns its actions with your intent. It’s a collaboration of human expertise and machine precision. The examples of AI agents in the enterprise world would be
Zapier: The Workflow Choreographer:
Imagine a conductor orchestrating a symphony of tasks. That’s Zapier—an AI agent that harmonizes your favorite apps. With a few clicks, you connect Gmail, Slack, Trello, and more. No coding required.
How It Works: Zapier listens for triggers (e.g., a new email arrives), then performs actions (e.g., adds a task to your to-do list). It’s like teaching a musical instrument to play itself.
Microsoft Power Apps: The Canvas Composer:
Picture a blank canvas waiting for your brushstrokes. Microsoft Power Apps invites you to create mobile apps, dashboards, and forms. Drag and drop UI elements, add logic, and voilà!
How It Works: You design screens visually, define data sources, and add business logic. The AI agent translates your vision into functional apps. No coding expertise needed.
Shopify: The E-Commerce Virtuoso:
E-commerce entrepreneurs, meet your backstage assistant. Shopify simplifies online store creation. Customize themes, manage inventory, and track orders—all through an intuitive interface.
How It Works: Shopify’s AI agent handles product listings, payments, and inventory updates. It’s like having a tireless shopkeeper who never forgets a customer’s preferences.
Difference between AI Agents, LLMs & RAG
The key distinction between AI agents and large language models (LLMs) or retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) models lies in their capabilities. AI agents combine the power of LLMs with additional components like memory, reasoning, and task-specific tools. They are designed to perform intricate tasks by breaking them down into smaller steps, maintaining context, and leveraging RAG-like mechanisms to retrieve relevant information when needed. However, AI agents go beyond RAG by incorporating memory, reasoning, and the ability to utilize various tools to accomplish tasks that require multiple steps or external data sources.
AI Agents in Enterprise Applications
When deploying AI agents in an enterprise, focus on three critical areas1:
1. Accuracy and Performance Metrics
Evaluating accuracy, efficiency (duration, tokens, messages), and cost provides insights into the agent's capabilities, resource utilization, and economic viability.
- Accuracy: Percentage of questions/tasks answered or performed correctly by the agent.
- Duration: Average time taken by the agent to answer a question or complete a task.
- Tokens/Messages: Average number of tokens or messages required by the agent per question/task.
- Cost: Average cost incurred in using the agent per question/task.
2. Humanized Interaction and User Experience
Evaluating naturalistic interactions and user experience is crucial for agents designed to interact with humans in a seamless and intuitive manner.
- Standardized Test Suites: Evaluating the agent's ability to interact naturally by replaying real human interaction scenarios and assessing its continuations.
- Human Evaluation: Involving diverse human evaluators to assess the agent's outputs, decisions, and interactions for humanized response naturally, appropriateness, and user experience.
3. Ethical Considerations and Robustness
- Bias and Fairness: Evaluating the agent's outputs and decisions for potential biases against specific demographics or groups.
- Transparency and Explainability: Assessing the interpretation and explainability of the agent's decision-making processes.
- Robustness and Security: Evaluating the agent's resilience against malicious attacks, data manipulation, data poisoning, and system failures, as well as its adherence to security and privacy standards.
Open-Source AI Agents
If you’re eager to explore open-source AI agents2 and dive into their development, here are some exciting projects to consider:
1. AutoGPT
AutoGPT is an experimental open-source project aimed at creating a fully autonomous AI agent capable of self-learning and self-improvement. It leverages large language models like GPT-3 and GPT-4 to perform a wide range of tasks without human intervention. AutoGPT has gained significant attention and is considered one of the pioneering projects in the field of autonomous AI agents.
2. AutoGen
AutoGen is an open-source framework developed by Microsoft in collaboration with OpenAI, Penn State University, and the University of Washington. It enables the development of AI agents that can engage in multi-agent conversations to solve tasks. AutoGen agents are customizable, conversable, and allow seamless human participation, making it a powerful platform for building advanced AI applications.
3. Baby AGI
Baby AGI is another notable open-source project focused on developing an autonomous AI agent with general intelligence capabilities. Similar to AutoGPT, it combines large language models with memory, reasoning, and external tool integration to accomplish complex tasks.
Conclusion
Ultimately, I believe that AI agents will become powerful tools that enables human to focus on strategic work, freeing us from tedious tasks and enabling us to focus on more being creative.
However, their development and deployment must be guided by ethical principles, ensuring transparency, and alignment with human values, so that they remain under meaningful human control and serve the greater good of society.
Sources:
https://community.openai.com/t/evaluating-ai-agents-thoughts-on-this-flow/314663
https://aws.amazon.com/what-is/ai-agents/
https://every.to/napkin-math/what-are-ai-agents-and-who-profits-from-them